Revolutionary Discoveries: Harnessing Bone Marrow’s Exosomes
Introduction:
Bone marrow’s exosomes hold immense potential in the field of regenerative medicine, unveiling a new era of therapeutic possibilities. Understanding the significance of these tiny vesicles derived from bone marrow is crucial for unlocking their transformative power in healthcare.
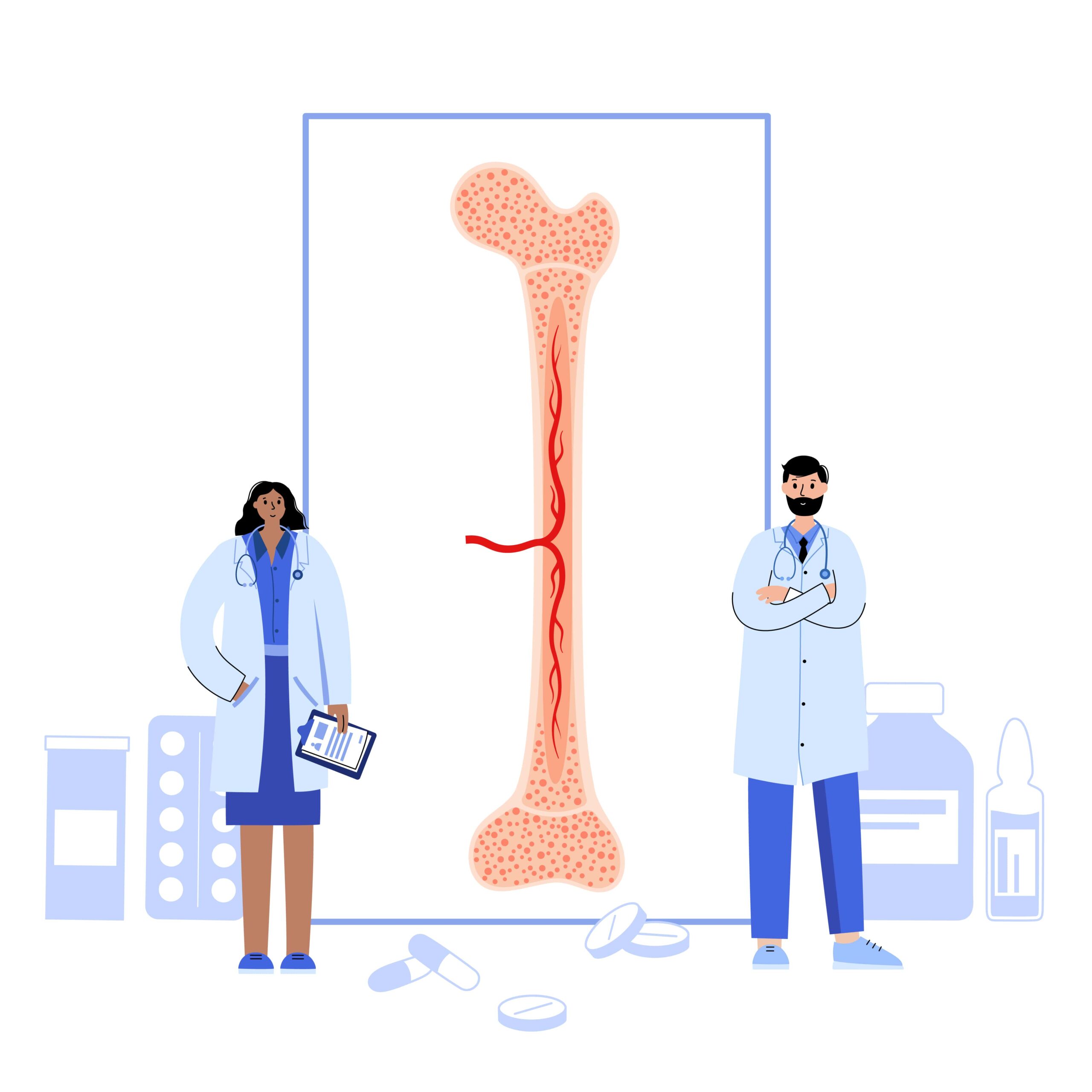
I. Exploring the Basics of Bone Marrow and Exosomes
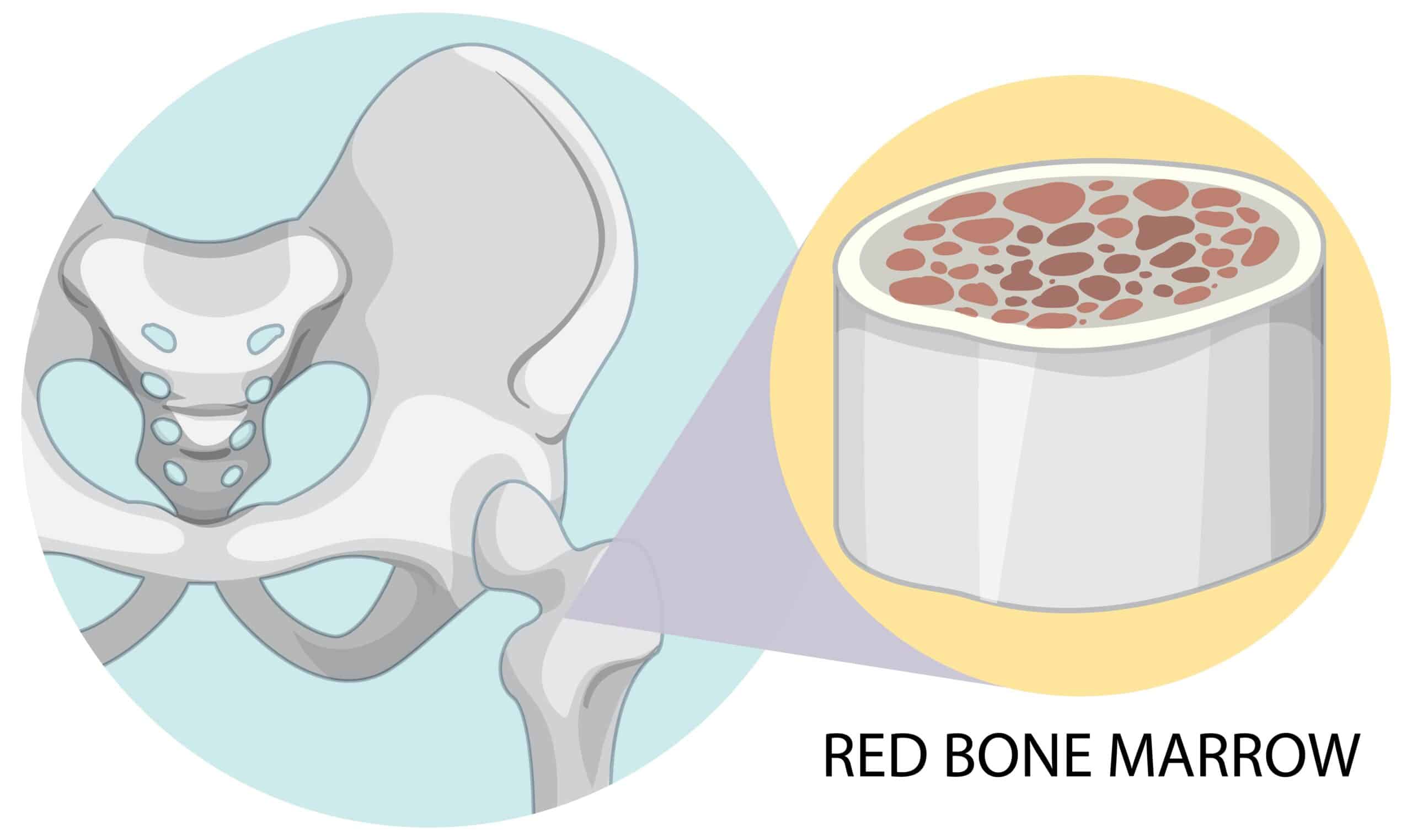
A. What is Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow, a spongy tissue found within our bones, is a complex microenvironment responsible for producing various components critical to our body’s functioning. Composed of hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells, stromal cells, and other cellular elements, bone marrow serves as a rich source of exosomes.

B. Unveiling Exosomes
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles, typically measuring 30-150 nanometers in diameter, secreted by cells. They carry a cargo of bioactive molecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, reflecting the cellular origin and playing a crucial role in intercellular communication.
II. The Fascinating Connection: Bone Marrow and Exosomes
A. How Bone Marrow Produces Exosomes
Exosomes originate from the endosomal system within bone marrow cells. The exosome biogenesis process involves the inward budding of the endosomal membrane, forming intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) within multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Upon fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane, exosomes are released into the extracellular space.
B. Interplay between Bone Marrow and Exosomes
Exosomes released by bone marrow cells traverse the bloodstream, lymphatic system, and other bodily fluids, enabling intercellular communication over long distances. These exosomes have a reciprocal relationship with bone marrow, influencing its functions, including hematopoiesis, immune regulation, and tissue repair.
III. Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Bone Marrow’s Exosomes
A. Role in Regenerative Medicine
Bone marrow-derived exosomes have emerged as promising agents for tissue repair and regeneration. Through their cargo of growth factors, cytokines, and miRNAs, exosomes modulate cellular processes, promote angiogenesis, and stimulate the migration and differentiation of target cells, facilitating tissue healing.
B. Advantages of Exosomes over Stem Cells
Exosomes offer several advantages over traditional stem cell therapies. Their non-invasive nature allows for targeted delivery, bypassing many challenges associated with transplantation. Furthermore, exosomes exhibit a lower risk of immunogenicity and tumorigenicity, addressing concerns associated with cell-based therapies.
![]()
![]()
IV. Cutting-Edge Research and Clinical Applications
A. Breakthrough Discoveries
Researchers have made remarkable strides in utilizing exosomes derived from bone marrow for treating neurological disorders. These tiny vesicles have shown potential in promoting neuronal survival, facilitating axonal regeneration, and enhancing synaptic plasticity. Additionally, exosomes hold promise in cardiovascular regeneration, stimulating tissue repair and improving cardiac function.
B. Clinical Trials and Success Stories
Clinical trials exploring the use of bone marrow-derived exosomes have yielded promising results. In the realm of bone regeneration, exosomes have shown the ability to enhance fracture healing and accelerate the formation of new bone tissue. Furthermore, exosomes have demonstrated efficacy in wound healing and dermatological conditions, improving tissue regeneration and promoting wound closure. In autoimmune diseases, exosomes exhibit the potential to modulate immune responses, reducing disease severity and enhancing treatment outcomes.
V. Unleashing the Future Potential
A. Innovative Techniques and Technologies
Researchers are actively investigating innovative techniques to engineer exosomes for enhanced therapeutic effects. These advancements aim to improve cargo loading, targeting specificity, and stability of exosomes, further augmenting their regenerative potential. Additionally, advancements in exosome isolation and characterization techniques enable a better understanding of their composition and function.
B. Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
Standardization and quality control are critical in harnessing the potential of exosome-based therapies. Establishing rigorous protocols for isolation, purification, and characterization is crucial for ensuring consistent therapeutic outcomes. Simultaneously, developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks and addressing ethical considerations surrounding exosome-based therapies is paramount to their safe and responsible implementation.
VI. The Road Ahead: Implications and Opportunities
A. Transforming Medical Paradigms
The emergence of bone marrow-derived exosomes has the potential to revolutionize medical practices. Personalized medicine and tailored therapies can be developed by harnessing the unique properties of exosomes, allowing for precise disease targeting and customized treatments. Furthermore, exosomes are poised to revolutionize drug delivery systems, enabling more efficient and targeted administration of therapeutics.
B. Collaborative Research and Partnerships
The future of exosome research lies in collaborative efforts between academia and industry. By fostering partnerships and cross-disciplinary approaches, researchers can leverage diverse expertise and resources to accelerate advancements in the field. Such collaborations will drive innovation, enhance knowledge exchange, and expedite the translation of exosome-based therapies from the lab to the clinic.
Conclusion:
Embracing the potential of bone marrow’s exosomes opens up a world of possibilities in regenerative medicine. With their ability to promote tissue repair, modulate immune responses, and stimulate cellular regeneration, these tiny vesicles hold the key to a healthier future. By continuing to explore their therapeutic potential, standardizing their production and delivery, and nurturing collaborative efforts, we pave the way for a new era of medical breakthroughs and improved patient outcomes.