Alleviate Arthritis Symptoms with Autologous Exosomes
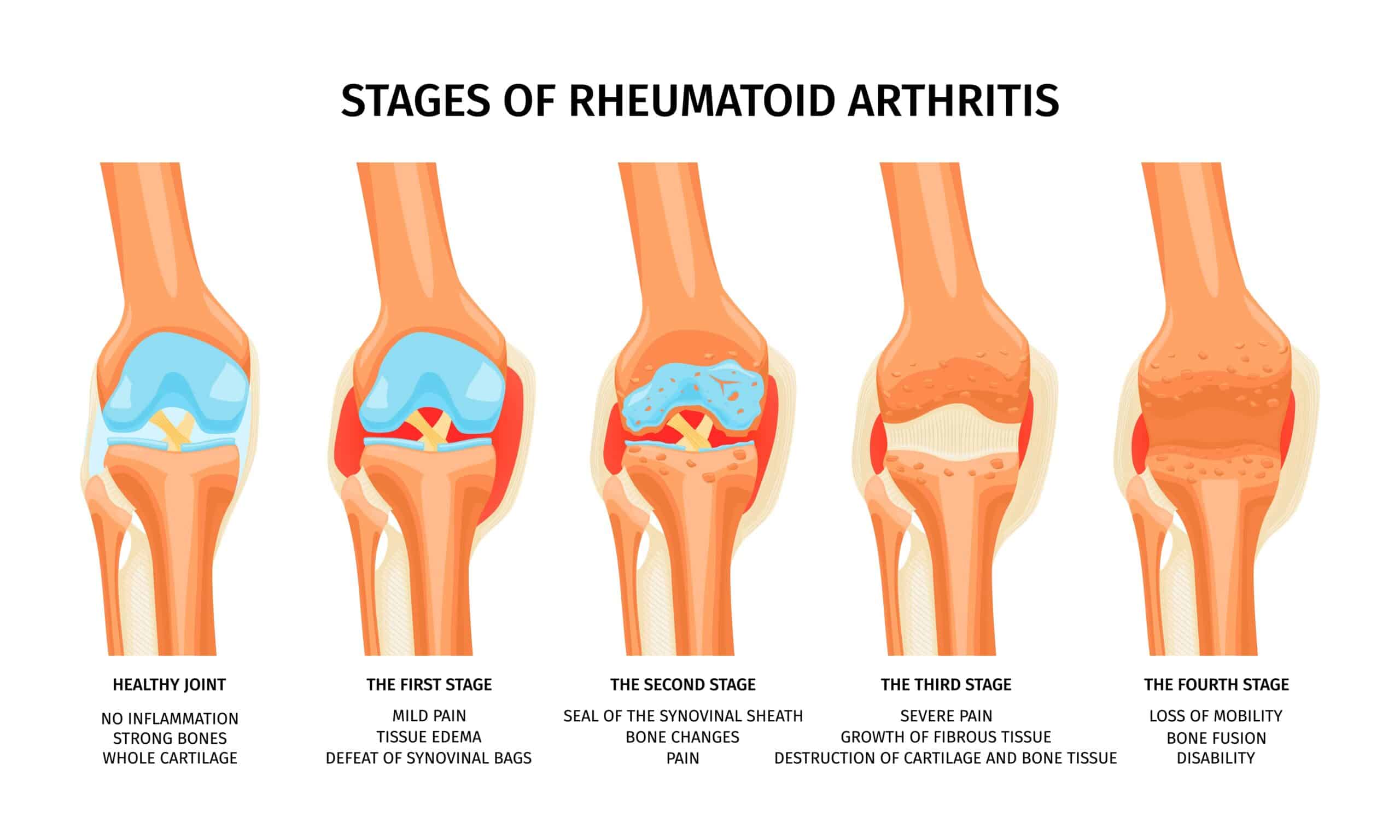
Introduction
Arthritis is a debilitating condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, causing joint inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Traditional treatment options aim to manage symptoms and slow down disease progression. But recent advancements in regenerative medicine have brought about a potential breakthrough in arthritis therapy: autologous exosomes. These tiny vesicles, derived from the patient’s own cells, hold immense promise in alleviating arthritis symptoms. Also improving the quality of life for those living with this chronic condition.
Understanding Autologous Exosomes
Autologous exosomes are small, membrane-bound vesicles that originate from the patient’s own cells. These remarkable entities act as messengers, carrying vital cargo of proteins, lipids, and genetic material. They play a pivotal role in intercellular communication and regulate various cellular processes. Autologous exosomes are obtained through a meticulous process that involves isolating and purifying them from the patient’s own cells. Ensuring compatibility and minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Autologous exosomes possess unique properties that make them an ideal therapeutic option for arthritis. Their small size enables them to penetrate deep into tissues, delivering their beneficial cargo to the affected joints. Additionally, these exosomes exhibit stability and are capable of withstanding harsh conditions, ensuring their effectiveness in the treatment process.
The Role of Autologous Exosomes in Arthritis
Autologous exosomes exert their therapeutic effects by addressing key aspects of arthritis pathogenesis. These tiny vesicles target the underlying mechanisms contributing to arthritis symptoms, leading to a comprehensive alleviation of pain and inflammation. The primary mechanisms of action include the reduction of inflammation and immune response, promotion of tissue repair and regeneration, and modulation of pain perception.
Inflammation is a hallmark of arthritis, causing joint swelling and discomfort. Autologous exosomes possess anti-inflammatory properties, effectively dampening the inflammatory cascade within the joints. By interacting with immune cells, these exosomes regulate the immune response, mitigating excessive inflammation. And facilitating a more balanced immune environment.
Furthermore, autologous exosomes play a crucial role in promoting tissue repair and regeneration. They contain bioactive molecules that stimulate the production of new cells and extracellular matrix components, aiding in the restoration of damaged joint tissues. This regenerative potential holds great promise for individuals suffering from arthritis. As it targets the root cause of the condition, facilitating long-term relief and improved joint function.
Additionally, autologous exosomes modulate pain perception in arthritis patients. By interacting with pain-sensing neurons, they influence the transmission of pain signals, leading to a reduction in pain intensity and improved pain management. This multimodal approach to addressing pain provides a holistic and comprehensive solution for individuals experiencing arthritis-related discomfort.

Research and Clinical Studies
Extensive research studies and clinical trials have been conducted to investigate the efficacy of autologous exosomes in arthritis treatment. These studies have yielded promising results, showcasing the potential of this innovative therapy. Clinical trials have demonstrated significant improvements in pain levels, joint function, and overall quality of life for individuals receiving autologous exosome treatment. Comparisons with traditional treatment options highlight the unique advantages offered by this regenerative approach, such as its ability to address the underlying disease mechanisms and promote sustained relief.
The Treatment Process
The administration of autologous exosomes for arthritis involves a comprehensive treatment process. Patient selection and eligibility criteria are crucial factors in determining the suitability of this therapy. Various factors, including disease severity, overall health, and responsiveness to previous treatments, are taken into consideration to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
The collection and isolation of autologous exosomes are performed through a meticulous procedure. This process involves obtaining a sample of the patient’s cells, such as mesenchymal stem cells, and isolating the exosomes through specialized techniques. Strict quality control measures are implemented to ensure the purity and viability of the exosomes, maximizing their therapeutic potential.
The administration of autologous exosomes can occur through different methods, tailored to the patient’s specific needs. Direct injection into the affected joints allows for targeted delivery, optimizing the therapeutic effects. Alternatively, systemic delivery through intravenous infusion ensures widespread distribution of the exosomes throughout the body. Dosage considerations are personalized for each patient, taking into account factors such as disease severity and treatment response.
While autologous exosome therapy is generally well-tolerated, potential side effects may occur. Commonly reported side effects include minor discomfort or temporary inflammation at the injection site. However, these effects are typically transient and resolve spontaneously. Close monitoring of patients throughout the treatment process allows for timely intervention and management of any adverse reactions.
Patient Experiences and Testimonials
Real-life stories of individuals who have undergone autologous exosome therapy for arthritis provide valuable insights into the potential benefits of this innovative treatment approach. Patients report significant improvements in pain management, increased joint mobility, and a renewed sense of well-being. These testimonials highlight the transformative impact autologous exosomes can have on daily life and overall functionality. The ability to regain mobility, engage in activities previously hindered by arthritis, and experience improved quality of life serves as a testament to the efficacy of this cutting-edge therapy.
Integrative Approaches to Arthritis Management
Complementary therapies and lifestyle modifications can further enhance the outcomes of autologous exosome therapy for arthritis. A comprehensive approach to arthritis management encompasses various facets that support the regenerative effects of autologous exosomes.
Exercise and physical therapy play a crucial role in maintaining joint flexibility, muscle strength, and overall functionality. Engaging in tailored exercise programs and physical therapy sessions helps individuals with arthritis optimize their joint mobility. As well as minimize joint stiffness, and improve their overall range of motion.
Nutrition and dietary adjustments can also contribute to arthritis management. Certain foods and dietary patterns have been associated with increased inflammation, exacerbating arthritis symptoms. By adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, individuals can help reduce inflammation and support the body’s healing processes.
Stress management techniques and relaxation practices can also positively impact arthritis symptoms. Chronic stress has been linked to increased inflammation and worsened pain perception. Incorporating mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals manage stress. But also promote emotional well-being, and enhance treatment outcomes.
Future Directions and Advancements
The field of autologous exosome therapy for arthritis is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research aiming to optimize treatment protocols and explore new possibilities. Collaboration between medical professionals, scientists, and industry experts is vital for advancing this cutting-edge field and improving patient care. Future directions include further refinement of treatment strategies, exploration of potential synergies with other innovative therapies. As well as development of novel delivery techniques.
Advancements in technologies and techniques for isolating and characterizing autologous exosomes continue to expand our understanding of their regenerative potential. Additionally, multidisciplinary approaches, involving the integration of various therapeutic modalities, hold great promise for enhancing treatment outcomes and providing comprehensive care for individuals with arthritis.
Conclusion
Autologous exosomes offer new hope for individuals suffering from the debilitating symptoms of arthritis. Their unique properties and regenerative potential make them a promising therapeutic option in the field of regenerative medicine. Research studies and clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of autologous exosome therapy in reducing pain, inflammation, and promoting tissue repair. As ongoing research progresses, the integration of autologous exosome therapy with complementary approaches, such as exercise, nutrition, and stress management, holds great promise for enhancing arthritis management and improving patients’ quality of life. With the potential to alleviate pain, restore joint function, and provide long-term relief, autologous exosome therapy offers a beacon of hope for those living with arthritis.